
Protect within
Only COSENTYX has long-term results in all 6 key clinical manifestations of PsA1-4
Unlike IL-23is, IL-17is, like COSENTYX, are recommended across all key clinical manifestations of PsA5
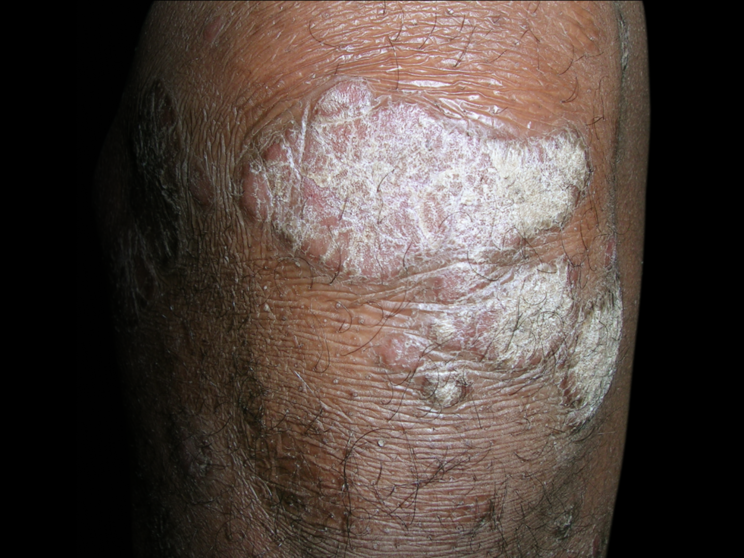
Skin
71% achieved PASI 90 at Year 2 in FUTURE 5 (n=68)1
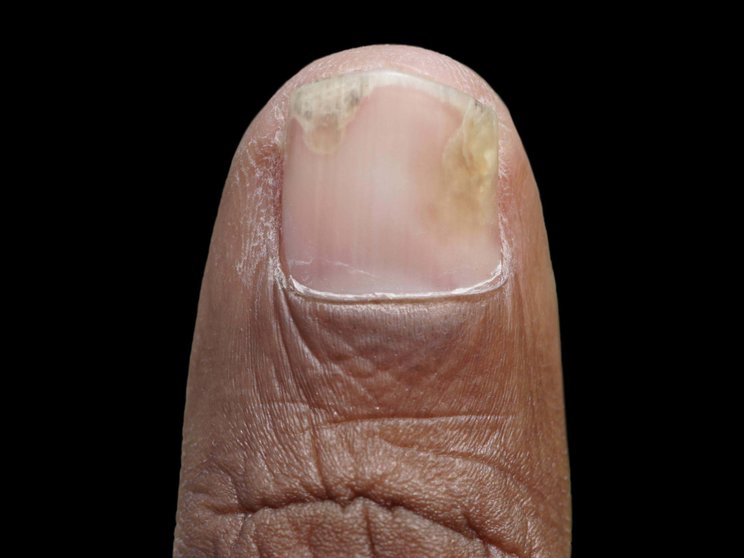
Nail
84% reduction in mNAPSI at Year 2 in FUTURE 5 (n=81)2
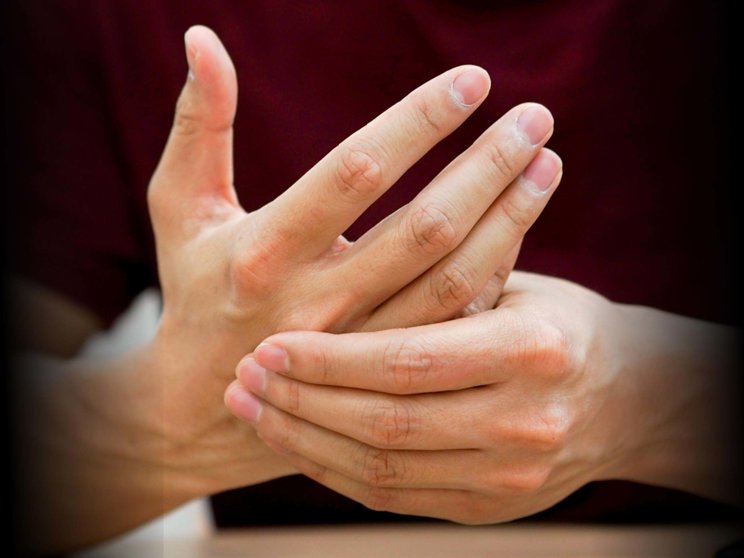

Joint
78% achieved joint relief at Year 2 in FUTURE 5 (n=137)3
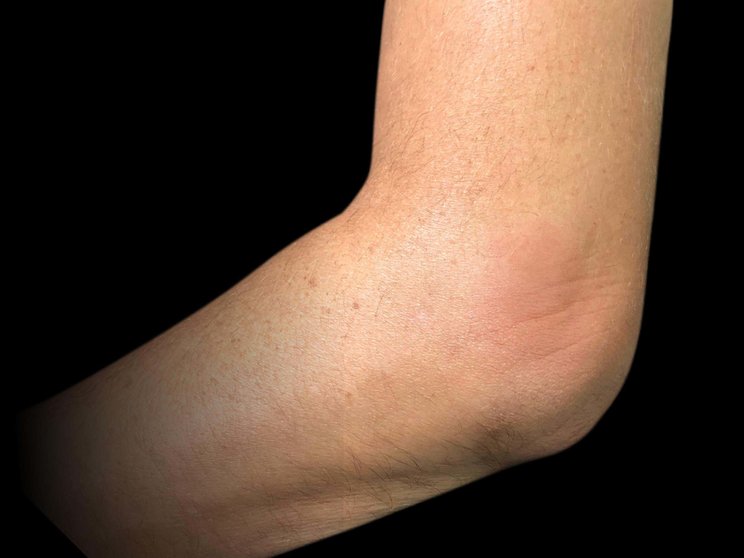
Enthesitis
80% achieved complete resolution at Year 2 in FUTURE 5 (n=88)3
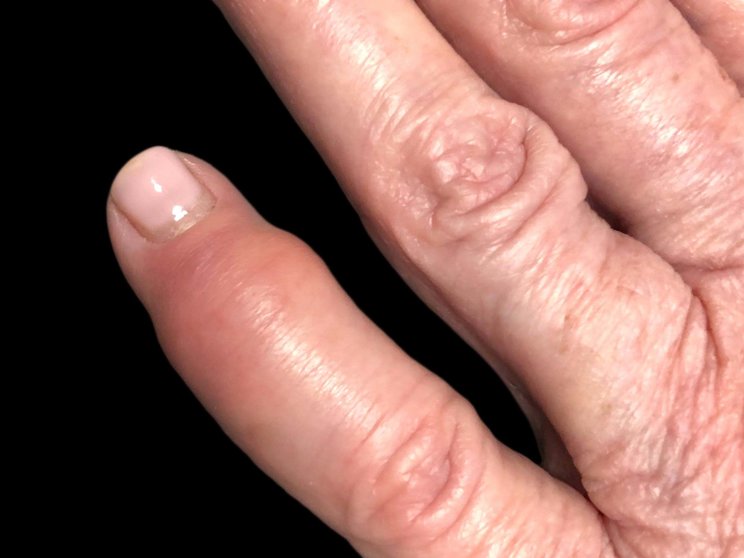
Dactylitis
88% achieved complete resolution at Year 2 in FUTURE 5 (n=48)3
Axial
81% achieved axial relief at Year 1 in MAXIMISE (n=139)4
Exploratory results at Year 2 (FUTURE 5) and Year 1 (MAXIMISE) with COSENTYX 300 mg in biologic-naive patients with PsA (as observed). No clinical or statistical conclusions can be drawn.1,4,6,7
Proven to help stop the progression of irreversible joint damage in PsA
At Year 2, 84% of patients* had no radiographic progression3†
COSENTYX 300 mg (n=139)

Gary, actual patient with PsO and PsA on COSENTYX, was compensated for his time. Individual results may vary.
No approved IL-23 inhibitor has been shown to stop further radiographic joint damage at 2 years8,9
*Biologic-naive patients.3
†No radiographic progression was defined as a change from baseline in mTSS ≤0.0.3
The only dedicated trial with proven results in axial manifestations4
MAXIMISE in biologic-naive patients with PsA4‡
ASAS20 responses at Week 12 (multiple imputation) were:
63% for COSENTYX 300 mg (n=164) (primary end point) (P<0.0001)
66% for COSENTYX 150 mg (n=157) (key secondary end point) (P<0.0001)
31% for placebo (n=164)
‡Data from the MAXIMISE trial, whose study design, patient population, and dosing regimen are consistent with those of FUTURE 2. In FUTURE 2, 20% of patients had spondylitis with peripheral arthritis.10
Definitions
IL, interleukin; IL-17i, interleukin-17 inhibitor; IL-23i, interleukin-23 inhibitor; mNAPSI, modified Nail Psoriasis Severity Index; mTSS, modified Total Sharp Score; PASI, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; PsA, psoriatic arthritis; PsO, plaque psoriasis.
References
1. Data on file. CAIN457F2342 (FUTURE 5): 2-Year Interim Report PASI 90 and ACR Components data. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; January 2020.
2. Data on file. CAIN457F2342 (FUTURE 5): 2-Year Interim Report. mNAPSI and PASI 100 data. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; October 2019.
3. Data on file. CAIN457F2342 (FUTURE 5): 2-Year Interim Report. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; May 2019.
4. Baraliakos X, Gossec L, Pournara E, et al. Secukinumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis and axial manifestations: results from the double-blind, randomised, phase 3 MAXIMISE trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(5):582-590.
5. Gossec L, Kerschbaumer A, Ferreira RJO, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies: 2023 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83(6):706-719.
6. Data on file. CAIN457F2342 Clinical Study Report. Interim Analysis-Week 24. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; November 2017.
7. Data on file. CAIN457F3302 (MAXIMISE): 1-Year Clinical Study Report. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; August 2020.
8. Clinicaltrials.gov. Absence of radiographic progression data at 2 years for IL-23 inhibitors in PsA. Completed March 24, 2025.
9. Clinicaltrials.gov. A study of guselkumab in participants with active Psoriatic arthritis (APEX). NCT04882098. Accessed September 24, 2025. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04882098
10. Cosentyx. Prescribing information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.
